People tend to think of memories as deeply personal, ephemeral possessions — snippets of emotions, words, colors and smells stitched into our unique neural tapestries as life goes on. But a strange series of experiments conducted decades ago offered a different, more tangible perspective. The mind-bending results have gained unexpected support from recent studies.
In 1959, James Vernon McConnell, a psychologist at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, painstakingly trained small flatworms called planarians to associate a shock with a light. The worms remembered this lesson, later contracting their bodies in response to the light.
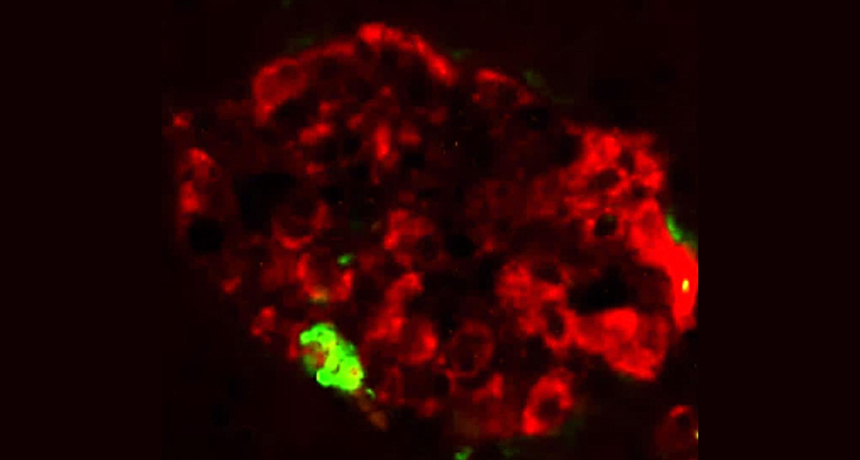
One weird and wonderful thing about planarians is that they can regenerate their bodies — including their brains. When the trained flatworms were cut in half, they regrew either a head or a tail, depending on which piece had been lost. Not surprisingly, worms that kept their heads and regrew tails retained the memory of the shock, McConnell found. Astonishingly, so did the worms that grew replacement heads and brains. Somehow, these fully operational, complex arrangements of brand-spanking-new nerve cells had acquired the memory of the painful shock, McConnell reported.
In subsequent experiments, McConnell went even further, attempting to transfer memory from one worm to another. He tried grafting the head of a trained worm onto the tail of an untrained worm, but he couldn’t get the head to stick. He injected trained planarian slurry into untrained worms, but the recipients often exploded. Finally, he ground up bits of the trained planarians and fed them to untrained worms. Sure enough, after their meal, the untrained worms seemed to have traces of the memory — the cannibals recoiled at the light.
The implications were bizarre, and potentially profound: Lurking in that pungent planarian puree must be a substance that allowed animals to literally eat one another’s memories.
These outlandish experiments aimed to answer a question that had been needling scientists for decades: What is the physical basis of memory? Somehow, memories get etched into cells, forming a physical trace that researchers call an “engram.” But the nature of these stable, specific imprints is a mystery.
Today, McConnell’s memory transfer episode has largely faded from scientific conversation. But developmental biologist Michael Levin of Tufts University in Medford, Mass., and a handful of other researchers wonder if McConnell was onto something. They have begun revisiting those historical experiments in the ongoing hunt for the engram.
Applying powerful tools to the engram search, scientists are already challenging some widely held ideas about how memories are stored in the brain. New insights haven’t yet revealed the identity of the physical basis of memory, though. Scientists are chasing a wide range of possibilities. Some ideas are backed by strong evidence; others are still just hunches. In pursuit of the engram, some researchers have even searched for clues in memories that persist in brains that go through massive reorganization.
Synapse skeptics
One of today’s most entrenched explanations puts engrams squarely within the synapses, connections where chemical and electrical messages move between nerve cells, or neurons. These contact points are strengthened when bulges called synaptic boutons grow at the ends of message-sending axons and when hairlike protrusions called spines decorate message-receiving dendrites.
In the 1970s, researchers described evidence that as an animal learned something, these neural connections bulked up, forming more contact points of synaptic boutons and dendritic spines. With stronger connection points, cells could fire in tandem when the memory needed to be recalled. Stronger connections mean stronger memory, as the theory goes.
This process of bulking up, called long-term potentiation, or LTP, was thought to offer an excellent explanation for the physical basis of memory, says David Glanzman, a neuroscientist at UCLA who has studied learning and memory since 1980. “Until a few years ago, I implicitly accepted this model for memory,” he says. “I don’t anymore.”
Glanzman has good reason to be skeptical. In his lab, he studies the sea slug Aplysia, an organism that he first encountered as a postdoctoral student in the Columbia University lab of Nobel Prize–winning neuroscientist Eric Kandel. When shocked in the tail, these slugs protectively withdraw their siphon and gill. After multiple shocks, the animals become sensitized and withdraw faster. (The distinction between learning and remembering is hazy, so researchers often treat the two as similar actions.)
After neurons in the sea slugs had formed the memory of the shock, the researchers saw stronger synapses between the nerve cells that sense the shock and the ones that command the siphon and gill to move. When the memory was made, the synapse sprouted more message-sending bumps, Glanzman’s team reported in eLife in 2014. And when the memory was weakened with a drug that prevents new proteins from being made, some of these bumps disappeared. “That made perfect sense,” Glanzman says. “We expected the synaptic growth to revert and go back to the original, nonlearned state. And it did.”
But the answer to the next logical question was a curve ball. If the memory was stored in bulked-up synapses, as researchers thought, then the new contact points that appear when a memory is formed should be the same ones that vanish when the memory is subsequently lost, Glanzman reasoned. That’s not what happened — not even close. “We found that it was totally random,” Glanzman says. “Completely random.”
Research from Susumu Tonegawa, a Nobel Prize–winning neuroscientist at MIT, turned up a result in mice that was just as startling. His project relies on sophisticated tools, including optogenetics. With this technique, the scientists activated specific memory-storing neurons with light. The researchers call those memory-storing cells “engram cells.”
In a parallel to the sea slug experiment, Tonegawa’s team conditioned mice to fear a particular cage and genetically marked the cells that somehow store that fear memory. After the mice learned the association, the researchers saw more dendritic spines in the neurons that store the memory — evidence of stronger synapses.
When the researchers caused amnesia with a drug, that newly formed synaptic muscle went away. “We wiped out the LTP, completely wiped it out,” says neuroscientist Tomás Ryan, who conducted the study in Tonegawa’s lab and reported the results with Tonegawa and colleagues in 2015 in Science.
And yet the memory wasn’t lost. With laser light, the researchers could still activate the engram cells — and the memory they somehow still held. That means that the memory was stored in something that isn’t related to the strength of the synapses.
The surprising results suggest that researchers may have been sidetracked, focusing too hard on synaptic strength as a memory storage system, says Ryan, now at Trinity College Dublin. “That approach has produced about 12,000 or so papers on the topic, but it hasn’t been very successful in explaining how memory works.”
Silent memories
The finding that memory storage and synaptic strength aren’t always tied together raises an important distinction that may help untangle the research. The cellular machines that are required for calling up memories are not necessarily the same machines that store memories. The search for what stores memories may have been muddled with results on how cells naturally call up memories.
Ryan, Tonegawa and Glanzman all think that LTP, with its bulked-up synapses, is important for retrieving memories, but not the thing that actually stores them. It’s quite possible to have stored memories that aren’t readily accessible, what Glanzman calls “occult memories” and Tonegawa refers to as “silent engrams.” Both think the concept applies more broadly than in just the sea slugs and mice they study.
Glanzman explains the situation by considering a talented violin player. “If you cut off my hands, I’m not able to play the violin,” he says. “But it doesn’t mean that I don’t know how to play the violin.” The analogy is overly simple, he says, “but that’s how I think of synapses. They enable the memory to be expressed, but they are not where the memory is.”
In a paper published last October in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Tonegawa and colleagues created silent engrams of a cage in which mice received a shock. The mice didn’t seem to remember the room paired with the shock, suggesting that the memory was silent. But the memory could be called up after a genetic tweak beefed up synaptic connections by boosting the number of synaptic spines specifically among the neurons that stored the memory.
Story continues below diagram
Those results add weight to the idea that synaptic strength is crucial for memory recall, but not storage, and they also hint that, somehow, the brain stores many inaccessible memory traces. Tonegawa suspects that these silent engrams are quite common.
Finding and reactivating silent engrams “tells us quite a bit about how memory works,” Tonegawa says. “Memory is not always active for you. You learn it, you store it,” but depending on the context, it might slip quietly into the brain and remain silent, he says. Consider an old memory from high school that suddenly pops up. “Something triggered you to recall — something very specific — and that probably involves the conversion of a silent engram to an active engram,” Tonegawa says.
But engrams, silent or active, must still be holding memory information somehow. Tonegawa thinks that this information is stored not in synapses’ strength, but in synapses’ very existence. When a specific memory is formed, new connections are quickly forged, creating anatomical bridges between constellations of cells, he suspects. “That defines the content of memory,” he says. “That is the substrate.”
These newly formed synapses can then be beefed up, leading to the memory burbling up as an active engram, or pared down and weakened, leading to a silent engram. Tonegawa says this idea requires less energy than the LTP model, which holds that memory storage requires constantly revved up synapses full of numerous contact points. Synapse existence, he argues, can hold memory in a latent, low-maintenance state.
“The brain doesn’t even have to recognize that it’s a memory,” says Ryan, who shares this view. Stored in the anatomy of arrays of neurons, memory is “in the shape of the brain itself,” he says.
A temporary vessel
Tonegawa is confident that the very existence of physical links between neurons stores memories. But other researchers have their own notions.
Back in the 1950s, McConnell suspected that RNA, cellular material that can help carry out genetic instructions but can also carry information itself, might somehow store memories.
This unorthodox idea, that RNA is involved in memory storage, has at least one modern-day supporter in Glanzman, who plans to present preliminary data at a meeting in April that suggest injections of RNA can transfer memory between sea slugs.
Glanzman thinks that RNA is a temporary storage vessel for memories, though. The real engram, he suggests, is the folding pattern of DNA in cells’ nuclei. Changes to how tightly DNA is packed can govern how genes are deployed. Those changes, part of what’s known as the epigenetic code, can be made — and even transferred — by roving RNA molecules, Glanzman argues. He is quick to point out that his idea, memory transfer by RNA, is radical. “I don’t think you could find another card-carrying Ph.D. neuroscientist who believes that.”
Other researchers, including neurobiologist David Sweatt of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, also suspect that long-lasting epigenetic changes to DNA hold memories, an idea Sweatt has been pursuing for 20 years. Because epigenetic changes can be stable, “they possess the unique attribute necessary to contribute to the engram,” he says.
And still more engram ideas abound. Some results suggest that a protein called PKM-zeta, which helps keep synapses strong, preserves memories. Other evidence suggests a role for structures called perineuronal nets, rigid sheaths that wrap around neurons. Holes in these nets allow synapses to peek through, solidifying memories, the reasoning goes (SN: 11/14/15, p. 8). A different line of research focuses on proteins that incite others to misfold and aggregate around synapses, strengthening memories. Levin, at Tufts, has his own take. He thinks that bioelectrical signals, detected by voltage-sensing proteins on the outside of cells, can store memories, though he has no evidence yet.
Beyond the brain
Levin’s work on planarians, reminiscent of McConnell’s cannibal research, may even prod memory researchers to think beyond the brain. Planarians can remember the texture of their terrain, even using a new brain, Levin and Tal Shomrat, now at the Ruppin Academic Center in Mikhmoret, Israel, reported in 2013 in the Journal of Experimental Biology. The fact that memory somehow survived decapitation hints that signals outside of the brain may somehow store memories, even if temporarily.
Memory clues may also come from other animals that undergo extreme brain modification over their lifetimes. As caterpillars transition to moths, their brains change dramatically. But a moth that had learned as a caterpillar to avoid a certain odor paired with a shock holds onto that information, despite having a radically different brain, researchers have found.
Story continues below box
Similar results come from mammals, such as the Arctic ground squirrel, which massively prunes its synaptic connections to save energy during torpor in the winter. Within hours of the squirrel waking up, the pruned synaptic connections grow back. Remarkably, some old memories seem to survive the experience. The squirrels have been shown to remember familiar squirrels, as well as how to perform motor feats such as jumping between boxes and crawling through tubes. Even human babies retain taste and sound memories from their time in the womb, despite a very changed brain.
These extreme cases of memory persistence raise lots of basic questions about the nature of the engram, including whether memories must always be stored in the brain. But it’s important that the engram search isn’t restricted to the most advanced forms of humanlike memory, Levin says. “Memory starts, evolutionarily, very early on,” he says. “Single-celled organisms, bacteria, slime molds, fish, these things all have memory.… They have the ability to alter their future behavior based on what’s happened before.”
The diversity of ideas — and of experimental approaches — highlights just how unsettled the engram question remains. After decades of work, the field is still young. Even if the physical identity of the engram is eventually discovered and universally agreed on, a bigger question still looms, Levin says.
“The whole point of memory is that you should be able to look at the engram and immediately know what it means,” he says. Somehow, the physical message of a memory, in whatever form it ultimately takes, must be translated into the experience of a memory by the brain. But no one has a clue how this occurs.
At a 2016 workshop, a small group of researchers gathered to discuss engram ideas that move beyond synapse strength. “All the rebels came together,” Glanzman says. The two-day debate didn’t settle anything, but it was “very valuable,” says Ryan, who also attended. He coauthored a summary of the discussion that appeared in the May 2017 Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. “Because the mind is part of the natural world, there is no reason to believe that it will be any less tangible and ultimately comprehensible than other components,” Ryan and coauthors optimistically wrote.
For now, the field hasn’t been able to explain memories in tangible terms. But research is moving forward, in part because of its deep implications. The hunt for memories gets at the very nature of identity, Levin says. “What does it mean to be a coherent individual that has a coherent bundle of memories?” The elusive identity of the engram may prove key to answering that question.